
About
Geothermal

Our mission is to empower homes and businesses with clean, renewable energy. We believe in reducing carbon emissions and lowering our dependence on non-renewable resources, and we are dedicated to making geothermal energy accessible to all. Here we'll dive into what geothermal is and how it can benefit you.

What is Geothermal?
Geothermal heating and cooling is a sustainable energy system that uses the natural heat storage capacity of the earth to heat and cool your home. It works by utilizing the relatively stable temperature of the earth just below the surface.
In the winter, the system extracts heat from the ground and transfers it to the building, providing warmth. In the summer, the process is reversed, with excess heat from the building being transferred to the ground for cooling. This is achieved through a network of underground pipes and a heat pump system.
Geothermal heating and cooling systems are extremely energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, as they rely on the earth's natural heat rather than burning fossil fuels.
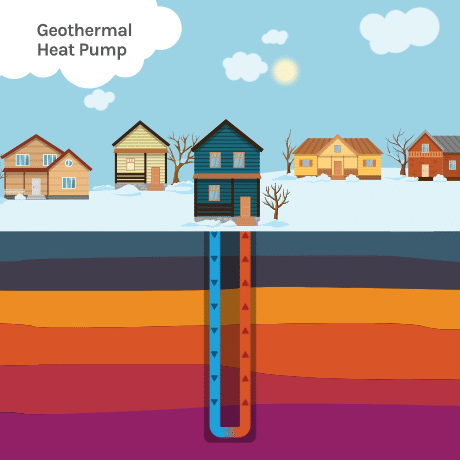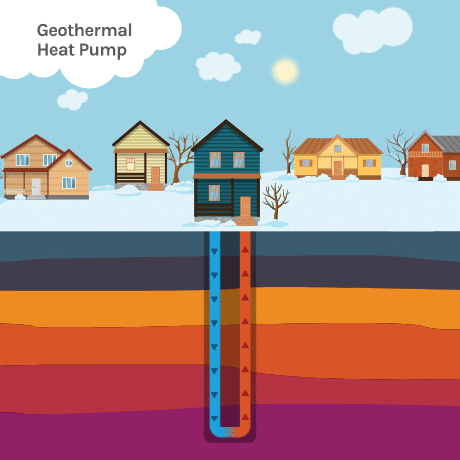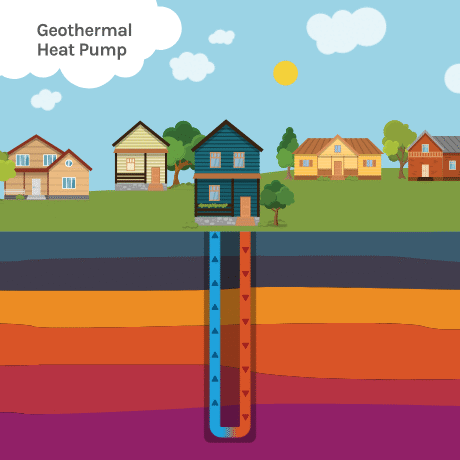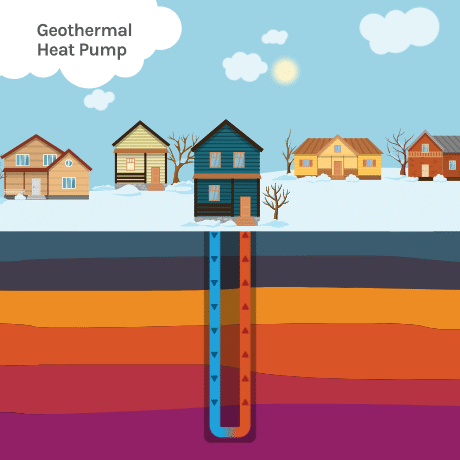
Geothermal Loop Systems
There are several types of geothermal loops used in geothermal heat pump systems to transfer heat between the ground and the building. The two main types of geothermal loops are:
-
Closed Loop Systems: In a closed loop system, a continuous loop of piping is buried underground or submerged in a body of water. There are two main variations of closed loop systems:
-
Horizontal Loops: These are used when sufficient land area is available for horizontal excavation. The piping is buried in trenches that vary in depth depending on the local climate.
-
Vertical Loops: When space is limited, vertical loops are used, with the piping installed in deep boreholes. This type of loop is more commonly used in urban or suburban areas where land area is limited.
-
-
Open Loop Systems: In an open loop system, groundwater is pumped from a well or other water source, used to transfer heat through a heat exchanger, and then discharged, typically into a drainage well or a body of water. Open loop systems are less common than closed loop systems and are typically not recommended.
Both closed loop and open loop systems allow for the transfer of heat between the ground and the home, with closed loop systems generally being more common due to their flexibility and potential lower environmental impact.
System Comparison
Geothermal heat pump (GSHP) systems are considered better than air source heat pump (ASHP) systems for several reasons.
-
Higher Efficiency: Geothermal heat pumps are known for their higher efficiency compared to air source heat pumps. This is because the ground or groundwater temperatures are relatively stable throughout the year, providing a more consistent heat source for heating and a heat sink for cooling. In contrast, air temperatures can vary significantly, especially in extreme climate conditions, leading to reduced efficiency of ASHPs under such circumstances.
-
Stable Performance: Geothermal systems have stable and consistent performance regardless of outdoor weather conditions, making them more reliable for heating and cooling purposes. ASHPs may experience reduced efficiency in very cold or very hot weather, affecting their performance and potentially increasing energy costs.
-
Longer Lifespan: Geothermal heat pumps have a longer lifespan compared to air source heat pumps. This is due in part to the fact that the ground loop components of geothermal systems are protected from outdoor elements and from wear and tear, leading to less maintenance and longer system longevity.
-
Lower Operating Costs: Geothermal systems offer lower operating costs over the system's lifetime. The higher efficiency and stability of geothermal heat pumps can result in lower energy bills and reduced overall operational expenses.
-
Environmental Impact: Geothermal systems are considered more environmentally friendly than air source heat pumps because they rely on the steady, renewable heat from beneath the Earth's surface rather than extracting heat from the outdoor air. This can lead to lower carbon emissions and reduced impact on the environment.